Welding has been around since ancient times. Read this article for a brief overview of welding history throughout the years.
Welding History: A Welding Timeline
Welding Town
The invention and technical production of welding is one of the most critical steps in metal fabrication and development as a modern society. The origins of welding date back thousands of years, with significant developments made across many continents. Welding is the original technique for humans to fuse metals together, leading to the production of utensils, jewelry, weapons, transportation, and more.
In the intricate tapestry of industrial evolution, welding stands as a testament to humanity’s innate desire to forge connections, both literally and metaphorically. This blog post delves into the captivating history of welding, tracing its origins, milestones, and the remarkable innovations that have shaped this indispensable craft.
The Ancient Origins
Welding’s roots can be traced back to ancient times, where skilled artisans and blacksmiths practiced forge welding. The fusion of metals was a meticulous process, a precursor to the modern techniques we now employ. As we explore the annals of welding, we encounter the sparks of creativity that ignited the forges of the past.
Anvil and Hammer: Birth of Forge Welding
In our exploration, we find that forge welding was the cornerstone of early metalworking. The rhythmic dance of the hammer and the anvil brought metals together, a symphony of craftsmanship that resonates through the ages.
Evolution in the Industrial Revolution
Fast forward to the Industrial Revolution, a pivotal era that witnessed the metamorphosis of welding. The advent of new technologies, such as the oxy-acetylene torch, revolutionized the landscape of metal joining, propelling welding into a new era.
The Oxy-Acetylene Torch: A Beacon of Progress
The Oxy-Acetylene torch emerged as a game-changer, providing unprecedented precision in welding. This marked a paradigm shift, enabling the creation of intricate metal structures and fueling the expansion of industries worldwide.
Welding in the Modern Era
As we step into the 20th century, welding becomes synonymous with technological prowess. The welding arc takes center stage, setting the tone for contemporary metalworking and construction practices.
The Welding Arc: Illuminating Possibilities
The discovery of the welding arc opened new frontiers. Electric arc welding techniques, including Stick and MIG welding, became the driving force behind skyscraper construction, shipbuilding, and the automotive industry.

Welding Today: A Fusion of Art and Science
In the 21st century, welding transcends its utilitarian roots, becoming an art form and a critical component of cutting-edge technology. From robotic welding arms on assembly lines to artistic sculptures, welding continues to shape our world in profound ways.
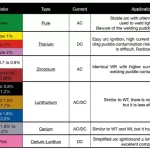
Who Invented Arc Welding?
The history of STICK Welding can be traced back to 1800s. In 1800, British chemist and inventor Sir Humphry Davy developed an arc between two carbon electrodes using a battery.
Gas welding and cutting was introduced in the mid-1800s. It was in the 1880s that arc welding with the carbon arc and metal arc was developed.
In 1881, French electrical engineer Auguste De Meritens used the heat of an arc to join lead plates for storage batteries. His student Nikolai N. Benardos was awarded a patent for welding. In 1890, C.L. Coffin of Detroit was granted the first U.S. patent for an arc welding process using a metal electrode.
Around 1900, British inventor Strohmenger introduced a coated metal electrode. He used a thin coating of clay or lime and noticed that it provided a more stable arc.
During the period of 1907 to 1914, Oscar Kjellberg of Sweden came up with a coated electrode which looked like a stick.
Later on, pieces of iron wire dipped in thick mixtures of carbonates and silicates were used to make stick electrodes.
Who Invented TIG Welding?
TIG welding was invented in 1941 by Russell Meredith of the Northrop Aircraft Corporation as a way to weld aluminum and magnesium in order to join light alloys used in aircraft manufacturing.
Union Carbide’s Linde division bought the rights to the GTAW welding patent and developed different torch designs under the “Heliarc” brand name. The first Heliarc machines were big transformer-rectifier-based and weighed hundreds of pounds.
During World War II, TIG welding became the preferred method to weld aircraft parts.
In the late 1970’s the Miller Company introduced the “square waveform” which allowed for much better arc control and smaller machines more suitable for AC applications.
With the introduction of printed circuit boards and inverter-style TIG machines, the adjustment capabilities and lighter weight gave way to the TIG welding method.
Who Invented MIG Welding?
MIG welding was developed in the 1940’s and 60 years later the general principle is still very much the same. MIG welding uses an arc of electricity to create a short circuit between a continuously fed anode (+ the wire-fed welding gun) and a cathode ( – the metal being welded).
The heat produced by the short circuit, along with a non-reactive (hence inert) gas locally melts the metal and allows them to mix together. Once the heat is removed, the metal begins to cool and solidify and forms a new piece of fused metal.
A few years ago the full name – Metal Inert Gas (MIG) welding was changed to Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW) but if you call it that most people won’t know what the heck your talking about – the name MIG welding has certainly stuck.
MIG welding is useful because you can use it to weld many different types of metals: carbon steel, stainless steel, aluminum, magnesium, copper, nickel, silicon bronze and other alloys.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Q1: What is the oldest known welding method?
A1: Forge welding, dating back to ancient times, holds the distinction as the oldest known welding method.
Q2: How did the Industrial Revolution impact welding?
A2: The Industrial Revolution ushered in technological advancements, with the oxy-acetylene torch being a key innovation that transformed welding processes.
Q3: What role did the welding arc play in the 20th century?
A3: The welding arc, a breakthrough in the 20th century, revolutionized metalworking, influencing industries such as construction, shipbuilding, and automotive manufacturing.
Q4: How has welding evolved in the 21st century?
A4: In the 21st century, welding has evolved into both an art form and a technological powerhouse, contributing to fields as diverse as robotics and sculpture.
Q5: Are there any famous welding projects?
A5: Yes, iconic projects like the Sydney Opera House and the Golden Gate Bridge showcase the transformative power of welding in large-scale constructions.
Conclusion
The journey through the history of welding is a fascinating exploration of human ingenuity. From the rhythmic beats of the ancient blacksmith’s hammer to the precision of modern welding arcs, each chapter in this narrative contributes to the rich tapestry of our industrial heritage. As we continue to push the boundaries of what is possible, welding remains an enduring symbol of our ability to forge connections and build the future.