If you’ve just entered the world of welding, then there’s at least one phrase you’ve probably already heard a few times: ‘TIG welding is hard.’
TIG welding might be harder than the other types of welding, but it isn’t an impossible task.
021208.com
Introduction
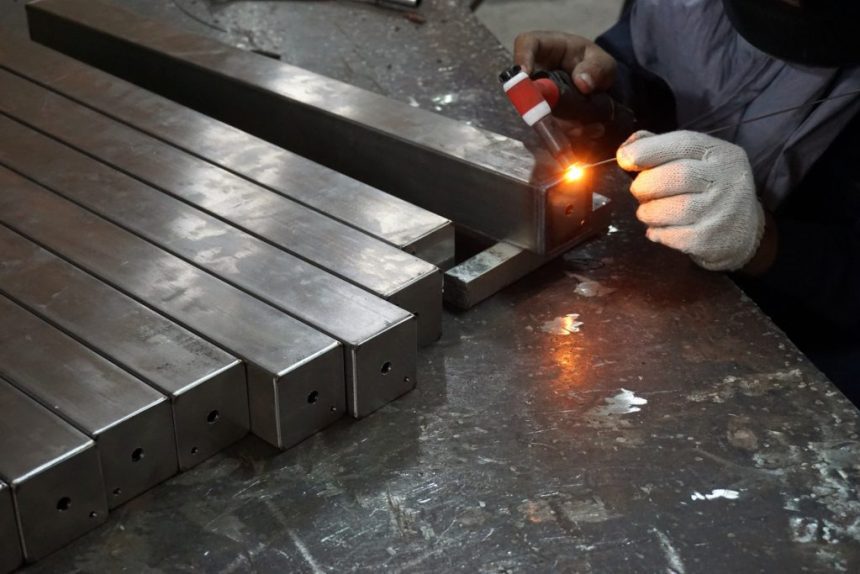
TIG welding, also known as Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW), is a popular welding technique used to create high-quality and precise welds. Whether you are a hobbyist or an aspiring professional welder, understanding the basics of TIG welding is essential. In this article, we will explore the fundamental aspects of TIG welding, providing you with the knowledge needed to get started in this versatile welding process.
What is TIG Welding?
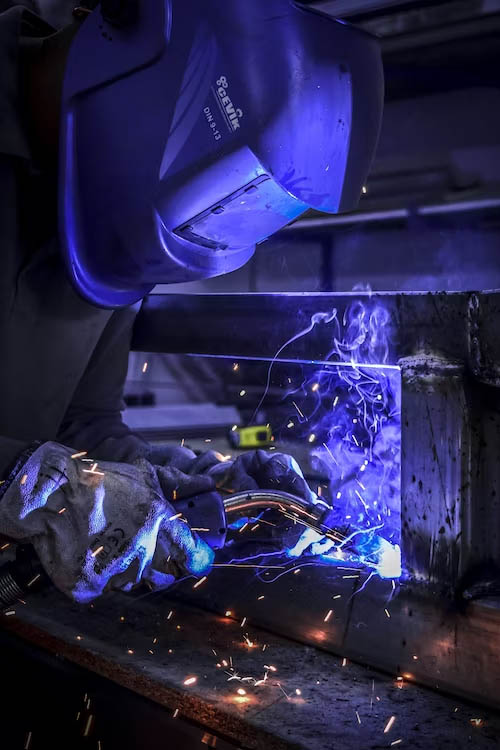
TIG welding is a welding process that utilizes a non-consumable tungsten electrode to create the weld. The electrode, along with a shielding gas, forms an arc that generates the heat required to melt the base metals. The filler material, if necessary, is added separately to create a strong and durable bond between the metals. TIG welding offers precise control over the heat input and produces clean welds with minimal spatter.
The Equipment Required for TIG Welding
Before diving into the intricacies of TIG welding, let’s first familiarize ourselves with the essential equipment needed for this process:
TIG Welder
A TIG welder, also known as a GTAW power source, is the core equipment for TIG welding. It provides the necessary current and voltage to strike and maintain the welding arc.
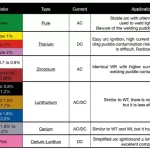
Tungsten Electrode
The tungsten electrode is a crucial component of TIG welding. It does not melt during the welding process and conducts the current to create the arc.
Shielding Gas
TIG welding requires a shielding gas, such as argon or a mixture of argon and helium, to protect the molten weld pool from atmospheric contamination.
Filler Material
In some cases, a filler material is required to reinforce the weld joint. The filler material is added manually using a separate filler rod.
Welding Torch
The welding torch holds the tungsten electrode and controls the flow of shielding gas. It also provides a means to guide the filler material, if necessary.
Advantages of TIG Welding
TIG welding offers several advantages that make it a preferred choice for various applications:
- Precision and Control: TIG welding allows for precise control over the heat input and welding parameters, resulting in highly accurate and clean welds.
- Versatility: TIG welding can be used on a wide range of materials, including stainless steel, aluminum, copper, and exotic metals.
- No Spatter: Unlike other welding processes, TIG welding produces minimal spatter, reducing the need for post-weld cleanup.
- No Flux: TIG welding does not require any flux, which simplifies the welding process and eliminates the need for flux removal.
- Weld Quality: TIG welding produces high-quality welds with excellent mechanical properties, making it suitable for critical applications.
If you start with the basics, you’ll be a pro in no time.
021208.com
Tips for TIG Welding Beginners
If you are new to TIG welding, here are some tips to help you get started:
- Proper Tungsten Selection: Selecting the appropriate tungsten electrode is crucial for achieving optimal results. Factors such as material type, thickness, and current requirements should be considered when choosing the electrode.
- Cleanliness is Key: Prior to welding, ensure that the base metal is clean and free from contaminants, such as oil, grease, and rust. Proper cleaning ensures better weld penetration and quality.
- Shielding Gas Flow: Maintain a consistent and adequate flow of shielding gas throughout the welding process to protect the weld zone from atmospheric contamination.
- Practice Tacking: Tacking, or making small welds to hold the workpieces together, helps in aligning and stabilizing the joint before the final welding. Practice tacking to improve your welding precision.
- Controlled Heat Input: TIG welding requires precise control over the heat input. Avoid excessive heat that can lead to distortion or burn-through, and aim for a uniform bead appearance.
Conclusion
TIG welding is a versatile and precise welding process that produces high-quality welds. With the right equipment, practice, and knowledge of the fundamental techniques, beginners can quickly master this welding technique. Remember to choose the appropriate tungsten electrode, maintain cleanliness, and practice proper welding techniques. By following these guidelines, you can embark on your TIG welding journey with confidence and create strong, visually appealing welds.
Now that you have a better understanding of TIG welding basics, it’s time to put your knowledge into practice and explore the endless possibilities this welding technique has to offer!