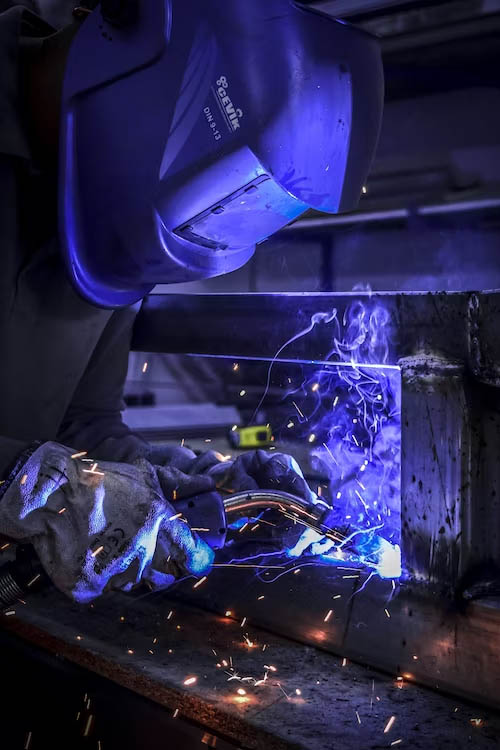
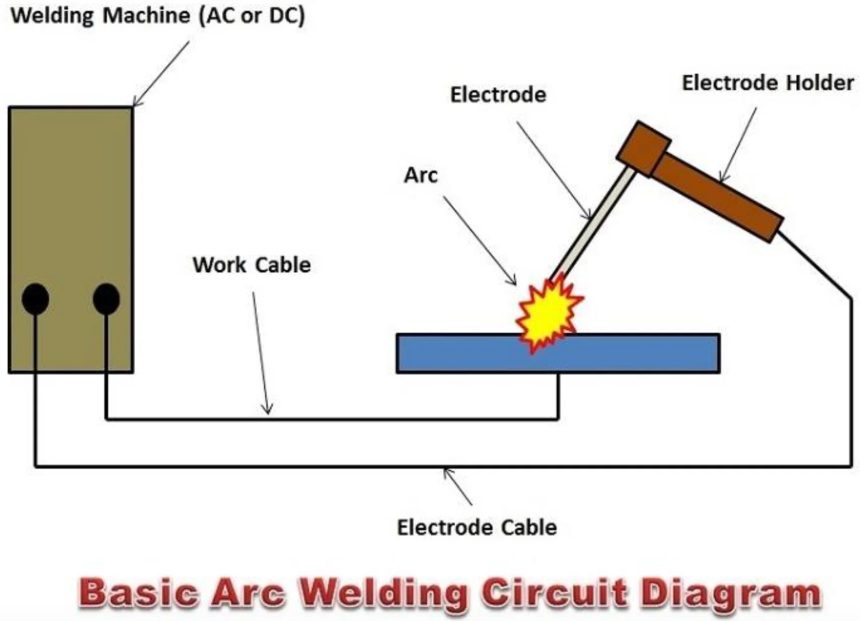
electricity to generate high levels of heat, which in turn melts the metals, creating a molten pool. As the metals cool and solidify, they fuse together, forming a single material. This fusion is the key factor behind the strength and durability of welded structures.
Arc welding is the process of melting two metals
Welding Town
Plasma arc welding
Plasma arc welding (PAW) is a welding process that offers several notable characteristics:
- Capability for thin and thick base metals: PAW can be used effectively on both incredibly thin and thick base metals, providing versatility in welding various materials.
- Non-consumable pointed tungsten electrode: Similar to TIG welding, PAW utilizes a non-consumable pointed tungsten electrode. However, in PAW, the electrode is positioned inside the torch, allowing for the separation of plasma and shield gas.
- High productivity: PAW offers a high productivity rate, making it suitable for applications that require efficient and rapid welding.
- Precise and accurate: PAW is known for its precise and accurate welding. The focused and powerful plasma arc enables fine control and results in high-quality welds.
- High-quality, attractive welds: PAW produces high-quality welds with an aesthetically pleasing appearance, making it suitable for applications where weld appearance is important.
- Difficult to master: Similar to other advanced welding processes, mastering PAW can be challenging and requires significant skill and expertise.
The Plasma arc welding process
The Plasma arc welding process involves the following steps:
- Plasma generation: Inside a PAW nozzle, gas is pressurized to create plasma. The plasma is then ionized to conduct electricity, generating an arc from the non-consumable pointed tungsten electrode.
- Arc power and control: The power of the arc can be adjusted by changing the voltage on the welding machine, providing control over the welding process.
- Shielding gas: A shielding gas, typically argon or hydrogen, surrounds the weld, protecting it from atmospheric contamination.
Where is Plasma arc welding used?
Plasma arc welding finds applications in various industries:
- Electronic applications: PAW is commonly used in electronic applications due to its precise and controlled welding capabilities.
- Aerospace, marine, and healthcare industries: The high precision of PAW makes it suitable for industries that require exceptional weld quality, such as aerospace, marine, and healthcare.
Plasma arc welding offers the advantages of precision, productivity, and high-quality welds, making it a valuable process in specialized applications.