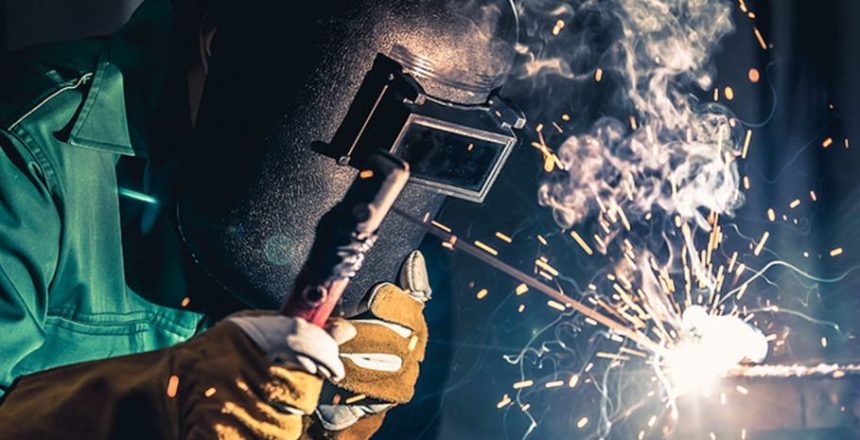
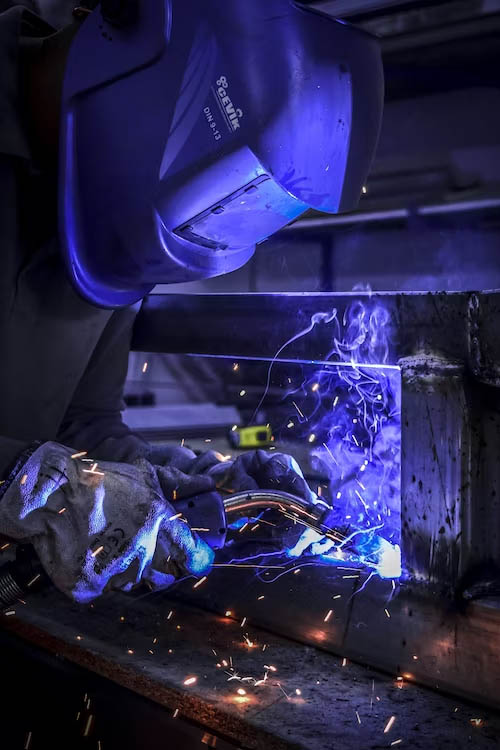
Stick welding, also known as Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW), is a popular welding process that is widely used in various industries. If you are a beginner looking to learn stick welding, this comprehensive guide will provide you with the necessary knowledge and tips to get started. Let’s dive in!
Beginner’s guide to stick welding (SMAW). Learn the essential equipment, techniques, and challenges associated with stick welding. Start your journey in the world of welding today!
021208.com
Understanding Stick Welding
Stick welding is a manual welding process that uses a consumable electrode coated with flux. The flux coating provides protection from atmospheric contamination and creates a slag layer that shields the weld pool. Stick welding can be performed on a variety of metals, including steel, stainless steel, and cast iron.
Equipment Needed
To begin your stick welding journey, you will need the following equipment:
- Welding machine: Choose a suitable welding machine that is compatible with stick welding. Consider factors such as amperage range, duty cycle, and portability.
- Electrodes: Select the appropriate electrodes based on the type of metal you are welding. Common electrode types include E6013, E7018, and E6010.
- Personal protective equipment (PPE): Ensure you have the necessary PPE, including a welding helmet, welding gloves, welding jacket, safety glasses, and welding boots. PPE is crucial for your safety during the welding process.
- Welding accessories: Gather other welding accessories such as electrode holders, welding cables, chipping hammers, wire brushes, and pliers.
Getting Started with Stick Welding
Follow these steps to begin your stick welding journey:
- Prepare the work area: Ensure you have a clean and well-ventilated work area. Remove any flammable materials and make sure you have a fire extinguisher nearby.
- Set up the welding machine: Connect the welding cables to the machine and secure the electrode holder. Adjust the machine settings based on the electrode diameter and material thickness.
- Prepare the metal: Clean the metal surface by removing any rust, paint, or debris. Use a wire brush or grinder for this purpose.
- Strike an arc: Position the electrode close to the workpiece and strike an arc by quickly tapping it against the metal. Once the arc is established, maintain a steady arc length of about 1/8 to 3/16 inch.
- Welding technique: Move the electrode in a controlled manner along the joint, maintaining a consistent travel speed. Pay attention to the angle and direction of the electrode to achieve the desired weld bead.
- Electrode manipulation: Practice various techniques such as drag, push, or circular motions to control the weld pool and penetration.
- Slag removal: After completing a weld, use a chipping hammer or wire brush to remove the slag and inspect the weld for any defects.
Tips for Successful Stick Welding
Here are some tips to improve your stick welding skills:
- Maintain proper electrode angle: Angle the electrode in the direction of travel for better penetration and control.
- Control travel speed: Maintain a steady and consistent travel speed to ensure proper fusion and avoid defects.
- Be mindful of amperage settings: Adjust the amperage based on the electrode size and metal thickness. Refer to the manufacturer’s recommendations for optimal settings.
- Practice good joint preparation: Clean and bevel the edges of the metal to create a suitable groove for the weld. Proper joint preparation ensures stronger welds.
- Learn from experienced welders: Seek guidance from experienced welders or enroll in welding classes to enhance your skills.
Common Stick Welding Challenges
Stick welding can present certain challenges, especially for beginners. Some common challenges include:
- Electrode sticking: To prevent electrode sticking, maintain the correct arc length and avoid excessive moisture in the electrode coating.
- Porosity: Porosity, or the presence of small holes in the weld, can occur due to improper shielding or contamination. Ensure proper electrode handling and cleanliness.
- Uneven weld bead: Inconsistent travel speed or improper manipulation of the electrode can result in an uneven weld bead. Practice maintaining a steady pace and proper electrode manipulation.
Conclusion
Stick welding is a versatile and widely used welding process that offers great flexibility and durability. By following the steps and tips outlined in this guide, beginners can start their stick welding journey with confidence. Remember to prioritize safety, practice proper technique, and continue learning from experienced welders. Happy welding!
Stick Welding for Beginners: A Comprehensive Guide to SMAW
021208.com
FAQs
Q1: Can I weld aluminum with stick welding? No, stick welding is not suitable for welding aluminum. Aluminum welding requires specialized equipment and processes such as Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG) welding.
Q2: Can stick welding be done outdoors? Yes, stick welding can be performed outdoors. However, it is important to consider wind conditions and take appropriate safety measures.
Q3: How long does it take to learn stick welding? The time required to become proficient in stick welding varies from person to person. With consistent practice and dedication, beginners can acquire the necessary skills within a few months.
Q4: What are the advantages of stick welding? Stick welding is portable, cost-effective, and suitable for a wide range of applications and environments. It is also less sensitive to wind and weather conditions compared to other welding processes.
Q5: Is stick welding suitable for structural welding? Yes, stick welding is commonly used for structural welding due to its versatility, ability to work with different metals, and excellent penetration capabilities.