Aluminum’s widespread use in modern manufacturing and fabrication industries is easily understandable due to its exceptional qualities. This lightweight, robust, and corrosion-resistant metal is favored across various applications, ranging from bicycles to spacecraft. Its appealing appearance and ease of machining further contribute to its popularity.
Weld Aluminum: Machine & Gear Checklist
Welding Town
Nevertheless, despite its impressive attributes, it’s crucial to acknowledge that aluminum can present challenges when it comes to welding, and it may not be compatible with certain welding techniques. Here’s what you need to be aware of regarding this remarkable material:
Why is aluminum welding so tricky?
Aluminum possesses a soft and insulated nature due to a thin aluminum oxide layer that melts at an exceptionally high temperature of 3,700°F (2,037°C), whereas aluminum itself melts at a much lower temperature of 1,200°F (650°C). Because the oxide layer melts at such a high temperature, it becomes imperative to remove it from the workpiece before initiating the welding process. Failure to remove the oxide layer would obstruct the formation of a connection between the arc and the weld pool. Ensuring thorough cleaning of the aluminum prior to welding not only eliminates the oxide layer but also eliminates any impurities like dirt and grease.
Another significant concern when welding aluminum is the issue of porosity. As the material heats up during welding, it quickly absorbs hydrogen. When the metal solidifies, the absorbed hydrogen separates, creating bubbles within the weld and leading to porosity issues. To minimize porosity, careful welding techniques and shielding gas selection are essential to reduce the hydrogen absorption and ensure a sound and structurally sound weld.
In summary, welding aluminum demands careful consideration and precise techniques. Removing the oxide layer through thorough cleaning and controlling hydrogen absorption can significantly improve the quality of the welds. By addressing these challenges, welders can achieve successful and reliable welds when working with this versatile and widely used metal.
What do I need to weld aluminum?
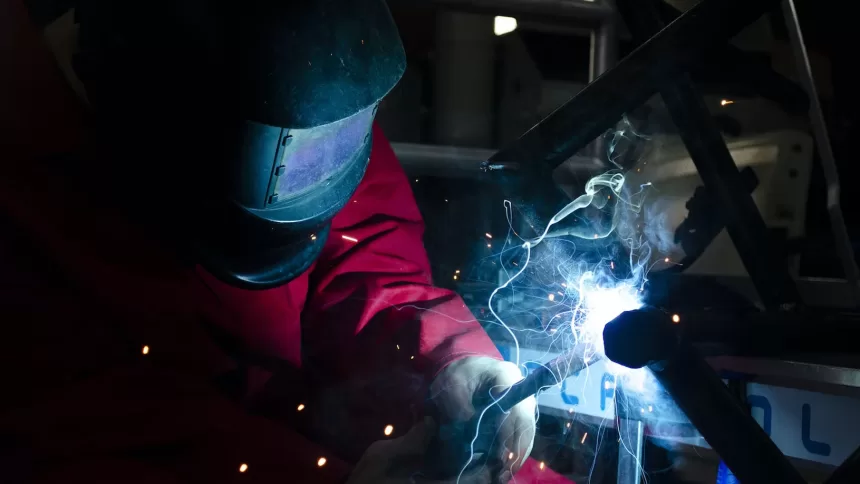
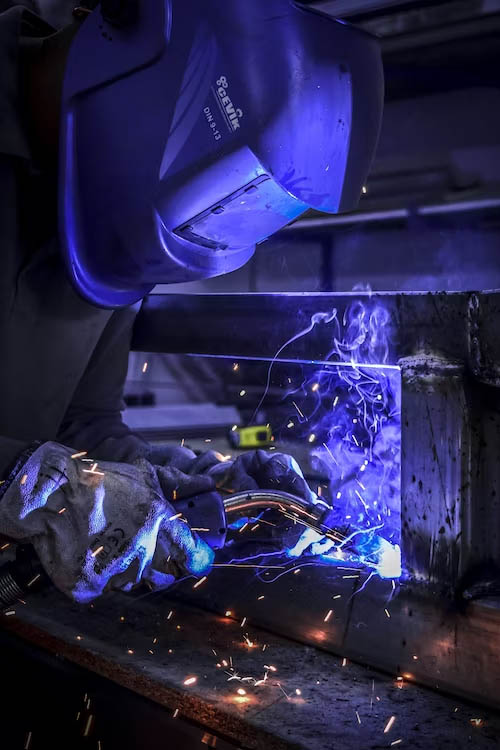
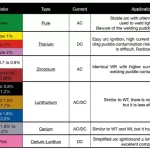
Welding aluminum is a distinctive process that differs from welding steel, which means that not all equipment is suitable for the task. To ensure successful aluminum welding and to mitigate inherent welding risks, it is essential to have the appropriate equipment and safety gear. Here is a checklist of the necessary machine and gear:
- Welding Machine: Choose a welding machine specifically designed for aluminum welding. Look for machines that offer adjustable amperage and pulse settings, as they are better suited to handle aluminum’s unique characteristics.
- TIG Torch: Utilize a TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) torch for precise control and a clean welding process. TIG welding is commonly preferred for welding aluminum due to its ability to provide better heat control and weld quality.
- Filler Material: Acquire the correct filler material that matches the grade and composition of the aluminum being welded. Using the right filler metal is crucial for achieving strong and durable welds.
- Gas and Shielding: Ensure a suitable shielding gas, such as argon, is used during the welding process to protect the weld zone from atmospheric contamination.
- Grinder or Wire Brush: Have a grinder or wire brush on hand to remove the thin oxide layer from the aluminum surface before welding. This step is crucial to promote proper bonding and prevent defects in the weld.
- Safety Equipment: Prioritize safety by wearing the appropriate safety gear, including:
- Welding Helmet: Use a helmet with a shade suitable for aluminum welding to protect eyes from intense light and harmful UV rays.
- Welding Gloves: Invest in heat-resistant and insulated gloves to shield hands from heat and sparks.
- Welding Apron or Jacket: Wear a flame-resistant apron or jacket to protect against spatter and potential burns.
- Respirator: Use a respirator to prevent inhalation of fumes and gases generated during welding.
- Welding Curtain or Screen: Set up a welding curtain or screen to protect nearby personnel from welding sparks and UV radiation.
By following this machine and gear checklist, welders can ensure that they have the appropriate tools to tackle aluminum welding effectively and safely. Equipping oneself with the right equipment enhances the welding experience and contributes to achieving high-quality and reliable welds.